Key Takeaways
- The Bank of Japan has made a significant decision to raise interest rates after maintaining them at a negative level since 2016. This move, the first increase in over a decade, signals a notable change in the bank’s approach to monetary policy.
- Governor Kazuo Ueda of the Bank of Japan has expressed optimism about achieving the target inflation rate of 2% in a sustainable and stable manner. This positive outlook reflects confidence in Japan’s inflation trends.
- Despite the interest rate hike, the Bank of Japan intends to keep monetary conditions accommodating to support economic growth and price stability. This indicates a cautious attitude towards further tightening measures.
- The Bank of Japan is willing to explore various options for easing monetary policy, including revisiting past strategies if necessary. This flexibility demonstrates its readiness to respond to evolving economic circumstances.
- The recent wage negotiations play a crucial role in shaping future rate decisions, as wage growth is seen as tied to potential increases in interest rates.
- Acknowledging the risks associated with sudden surges in interest rates, the Bank of Japan is adopting a prudent and gradual approach towards any future policy adjustments.
- Changes are being considered within the framework of monetary policy for after announcing the changes, they decided to stop buying ETFs and Japan REITs, with plans to gradually decrease and eventually stop purchasing corporate bonds within a year. They will continue buying JGBs at a similar rate as before.
- In response to the policy updates, the Japanese Yen weakened against the US Dollar, leading to the USD/JPY pair reaching the 150.00 level, showing a ‘sell the fact’ reaction in the market.
- Looking ahead, the BoJ anticipates Japan’s economy will keep improving steadily, expecting CPI to remain above 2% until fiscal 2024, reflecting their confidence in Japan’s economic foundation.
- Despite their optimism, the BoJ acknowledges significant uncertainties surrounding Japan’s economy and prices. They are committed to closely monitoring market trends, FX impacts and maintaining flexibility in their policy decisions.
Impacts and Analysis
The recent decision to increase interest rates after a long span of 17 years marks a significant shift in its monetary policy, moving away from the era of extremely low or negative interest rates. This move, expected to take effect in the first half of 2024, could have far reaching consequences for both Japan’s economy and the global financial markets.
Impact on Japan’s Economy
The Bank of Japan’s move away from negative interest rates is part of a larger trend among central banks worldwide to tighten monetary policies in response to rising inflationary pressures. For Japan, this shift indicates a departure from strategies focused on combating deflation and promoting economic growth through ultra low borrowing costs. The policy adjustment is predicted to strengthen the yen, potentially alleviating inflationary pressures by reducing the cost of imports. Nevertheless, the transition may also result in higher borrowing expenses domestically, affecting both consumers and businesses that have become accustomed to low interest rates.
Implications for Japanese Banks
Japanese banks could experience varying effects from the increase in interest rates. On one hand, higher interest rates may enhance net interest margins, thus boosting banks profitability.
Concerns arise regarding the rise in credit costs and possible losses on bond investments as banks have substantial exposure to government and corporate bonds. The Bank of Japan’s adjustment to its yield curve control policy, allowing long term interest rates to increase while keeping short term rates low, presents a complex situation for the banking industry. This adjustment highlights the need for a cautious approach to monetary tightening, balancing economic stability with market functionality.
Implications on Global Markets
The potential end of Japan’s negative interest rate policy may have widespread effects on global financial markets, particularly impacting U.S. Treasurys. Since Japan holds a significant amount of U.S. Government securities, changes in its investment strategies in response to domestic rate hikes could influence global demand for U.S. Treasurys, potentially leading to higher yields in the U.S. Bond market. This scenario emphasizes how adjustments in one major economy can ripple through global financial systems.
The shift towards higher interest rates marks a significant change in policy for Japan, with its effects on both domestic and global markets unfolding gradually. It reflects the Bank of Japan’s response to evolving economic conditions and aligns with broader trends in global monetary policies.
Investors and policymakers will be keeping a close eye on this shift, assessing how it impacts economic growth, inflation and the stability of the banking sector in Japan and globally.
USD JPY and Nikkei Reactions
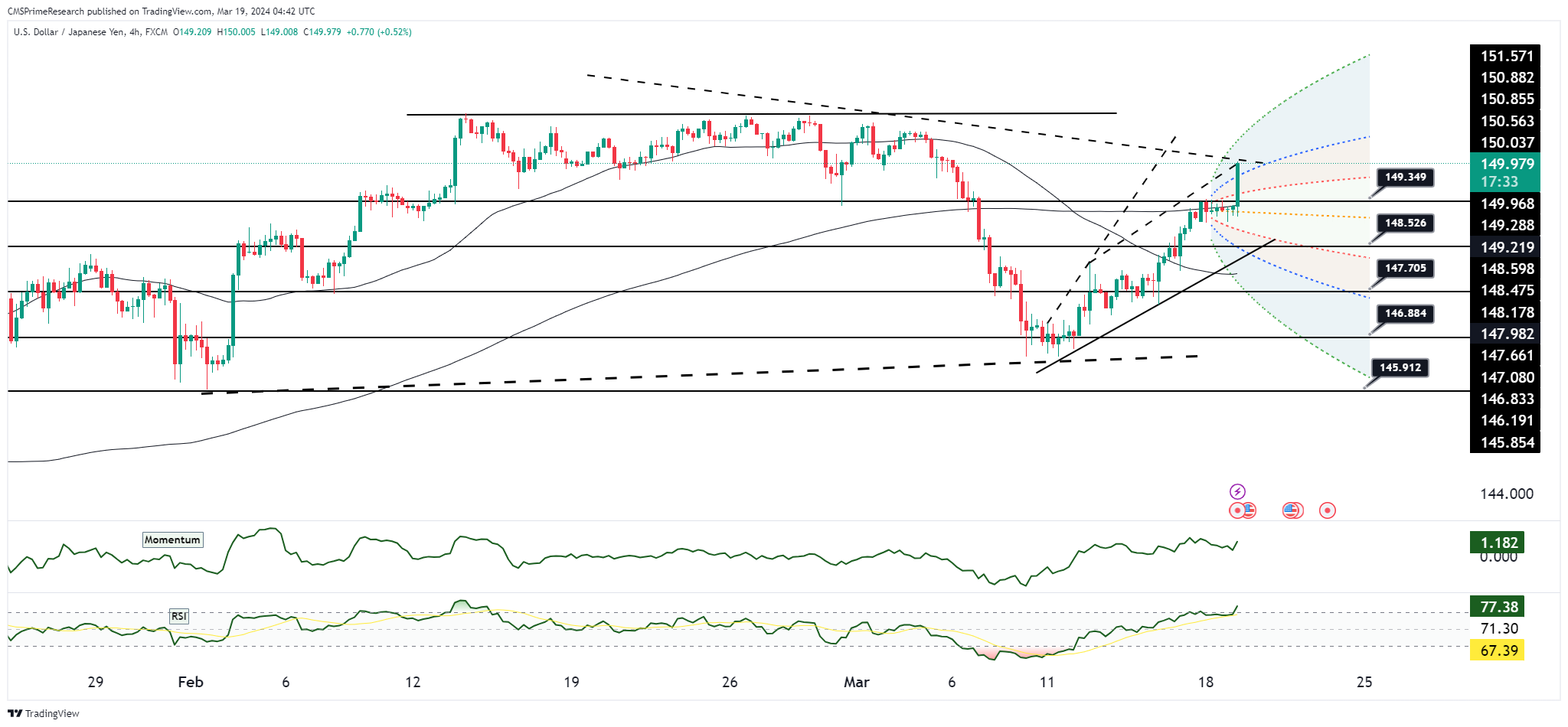
USD/JPY’s rebound in March could reach as high as 151, approaching the 2024 high of 150.88 and the 2022/23 peaks of 151.92/94, contingent on the Bank of Japan’s (BoJ) policy adjustments and the Federal Reserve’s stance on rate cuts. The currency pair has recovered significantly from its early March decline, which was evident of a BoJ rate hike—the first in 17 years—and fluctuating Fed rate cut expectations. The BoJ’s unexpected JGB purchases indicate a cautious approach to letting yields rise, even if it exits negative interest rates, thus minimizing yen repatriation risks. Should the upcoming Fed meeting not strongly support the likelihood of three rate cuts this year, USD/JPY could surpass its 20- and 50-day moving averages at 149.60/70, potentially testing the Fibonacci target of 151.2.
Japanese Stocks closed higher and Nikkei 225 Sees a 0.66% Increase. The support and resistance levels with current support (S3) at 30,266.6, medium support (S2) at 35,675.1, and near-term support (S1) at 38,099.8. The resistance levels are uniformly set at 40,571 for R1 through R3, indicating a strong resistance point that the index might test if the upward momentum continues. The Nikkei 225 is a “Strong Buy” based on an aggregate of technical indicators. Key insights include a “Buy” signal from 16 out of 21 indicators and a “Strong Buy” from 7 out of 21 indicators. Specific indicators such as the RSI (61.028), MACD (183.68), and the Bull/Bear Power (249.714) suggest buying, while the Stochastics indicator signals an overbought condition which could imply caution.
To know more about CMS Prime visit us at https://cmsprime.com
Disclaimer: This is not an Investment Advice. Investing and trading in currencies, CFD’s involve inherent risks. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and consider your risk tolerance before engaging in any financial activities.