Introduction:
Treasury yields have a great influence on currency prices because they are in tandem with interest rates and the health of a country’s economy. Treasury yields are usually a sign of a strong economy that tends to increase demand for that country’s currency. The currency will appreciate because of the high yields which will attract foreign investors who need to purchase the country’s currency to invest in the bonds thereby increasing demand and value of the currency. As another example, the U.S. bond yields give a hint as to the strength of the U.S. stock market and the dollar.
Furthermore, treasury yields are linked to the interest rates. Therefore, when the central bank increases interest rates, yields on government bonds also rise. When interest rates are higher, currency tends to be more attractive as investors get higher returns as they invest in interest bearing assets. This increased demand could lead to an appreciation of the currency.
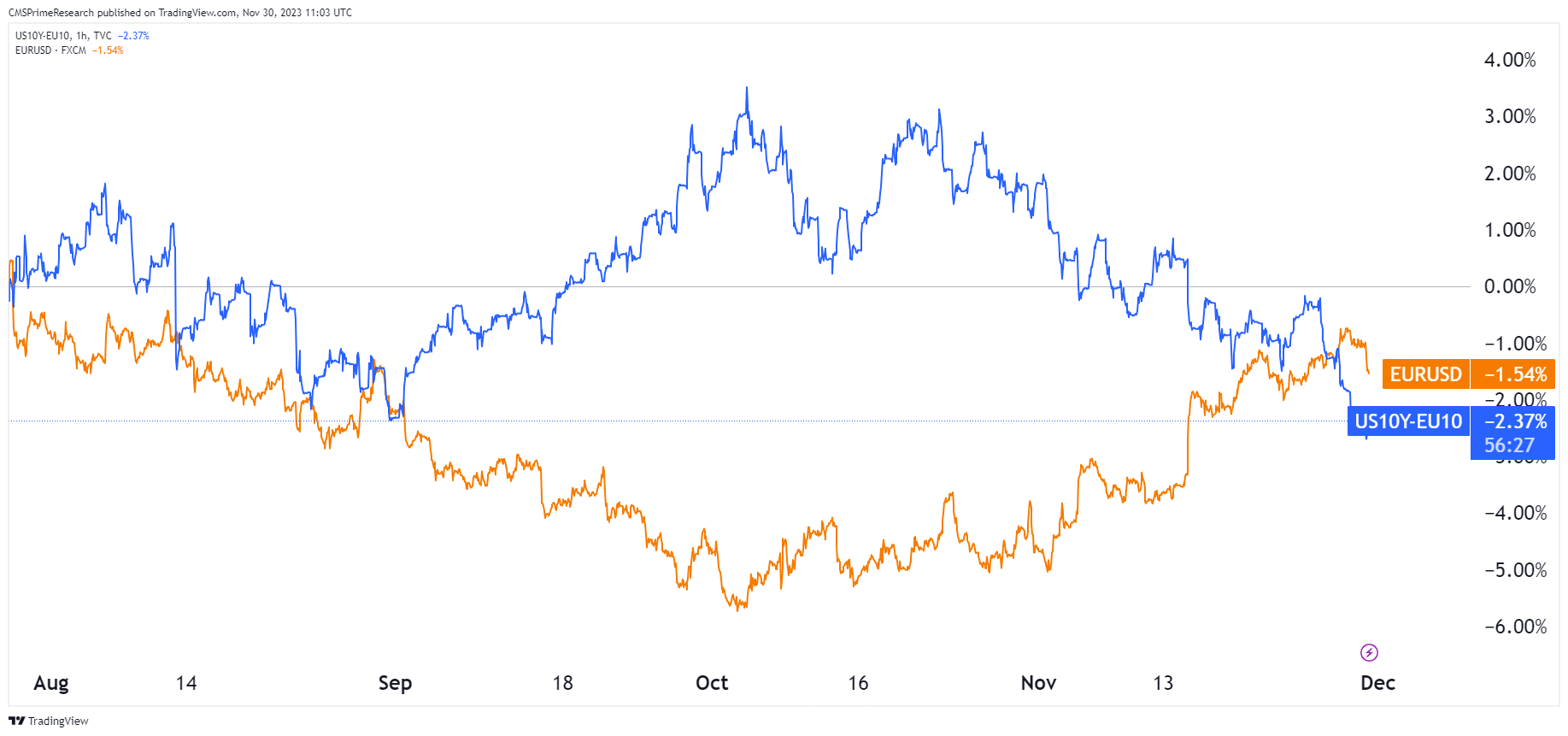
However, the movement of Treasury yields and currency prices may depend on other variables like inflation, economic performance, and market expectations. For example, if inflation is high, treasury yields can go up as a compensation for reduced purchasing power, and this may have effect on the currency. Likewise, market anticipations of future economic situations can affect both Treasury yields and currency prices.
Furthermore, it must be highlighted that correlation between Treasury yields and currency prices can differ from situation to situation, depending on economic characteristics of a given country. This is because, for instance, during economic uncertainty, most investors will seek to invest in safe-haven assets such as U.S. Treasury bonds, which will lead to a high demand for these bonds and a low supply, thus causing the bond prices to increase and the yields to decrease. In short, Treasury yields can have substantial impact on the currency prices, but it is very complicated and depends on many factors.
Decision Making and Evaluation Criteria
Bond yields are used when investors make decisions related to currency trading because bond yields give a reliable indication of the strength of the economy of a country and its stock market, which determines the demand for the country’s currency.
The relationship between bond yields and bond prices is inverse. Bond yields fall when bond prices rise, and bond prices rise when bond yields fall. This is crucial because it may point to changes in investor sentiments. For instance, when investors are concerned on the safety of their stocks investments, they move their money to bonds which pushes the bond prices higher and the bond yields down. The nation’s currency may appreciate as investors run to safer assets, in what is termed the “flight to safety”.
Another way to measure currency movements is the yield spread, which is the difference between bond yields of two given countries. Generally, when yield spread widen in favor of a certain currency, that currency appreciates against other currencies.
For example, if U.S. bond yields are higher than German bond yields, it could signal a stronger U.S. economy, which would boost the demand for the dollar and make it appreciate against the euro. However, a higher value of German bond yields may signal stronger German economy, which may lead to increased demand for euro causing appreciation against U.S. dollar.
Changes in bond yield are also monitored by investors, as they can represent altering rate expectations. For example, if bond yields rise, it may indicate that investors expect interest rates to increase leading to stronger currency. In conclusion, bond yields serve as an indicator for economic vitality, investor sentiments, and rate expectations that may influence currency changes and help make informed decisions for currency trading.
Intermarket Risk Perspective
Intermarket risk perspective on Treasury yields and currency prices involves the connection among different asset classes such as bonds, stocks, commodities, and currency, and how changes in one market may influence the others. Treasury yields, which are the interest rates on government bonds, can highly affect currency prices since they are related to interest rates and the condition of a country’s economy.
Investors analyze intermarket relationships between asset classes to detect economic trends and make informed decisions. For instance, when Treasury yields rise, it usually shows a strong economy that leads to a high demand for this country’s currency. Higher yields attract foreign investors who will purchase local currency for purchasing local bond. This increases the demand and value of the currency. In addition, treasury yields are highly correlated to interest rates, and where the central bank increases the interest rate, yields on government bonds increase and the currency becomes more attractive to foreign investors.
However, other factors such as inflation, economic growth, and market expectations can also affect the relationship between Treasury yields and currency prices. For example, if the inflation rate is high, Treasury yields could increase in order to make up for the reduction in buying capacity that leads to a devaluation of the currency. Moreover, market expectations regarding the future economic conditions may affect treasury yields and currency prices.
To conclude, the intermarket risk approach for Treasury yields and currency prices shows that different asset classes are inter-dependent and that the relationship between Treasury yields and currency prices is a function of interest rates, economic conditions, market expectations, and investor sentiments.
2 Facets to Consider
The Impact of Central Bank Policies on Treasury Yields and Currency Values
Central bank policies significantly influence Treasury yields and currency values through various channels. One crucial channel is the traditional interest-rate effects. Central banks, through their monetary policy actions, alter the interest rates, impacting Treasury yields directly. A lower interest rate typically results in lower Treasury yields, making bonds less attractive and possibly weakening the currency as investors seek higher returns elsewhere. Conversely, higher interest rates can increase Treasury yields, attracting more investment into bonds and potentially strengthening the currency.
Another significant transmission mechanism is through other asset price effects, notably the exchange rate effects on net exports and wealth effects. Monetary policy decisions can influence exchange rates, which then affect net exports and, consequently, aggregate demand. A stronger currency resulting from higher interest rates could reduce net exports, as domestic goods become relatively more expensive for foreign buyers. Similarly, monetary policy can impact wealth, particularly through asset prices like stocks, which again feeds into aggregate demand and currency value.
The Role of Global Economic Indicators and Events in Treasury Yield and Currency Fluctuations
Global economic indicators and events significantly impact Treasury yields and currency fluctuations. The balance sheet and cash flow channels play a pivotal role in this context. The balance sheet channel focuses on how monetary policy affects firms’ balance sheets, particularly in the context of net worth and its impact on borrowing and investment. For instance, a central bank’s easing policy that raises stock prices can increase firms’ net worth, potentially leading to higher investment spending and aggregate demand. This mechanism is particularly relevant in analyzing how global economic events and indicators, which can significantly impact stock prices and firms’ net worth, subsequently influence Treasury yields and currency values.
The cash flow channel, another aspect of the balance sheet mechanism, highlights how changes in monetary policy affect firms’ cash flows, crucial in determining their ability to service debts and invest. Lower interest rates improve balance sheets by increasing cash flow, enhancing firms’ liquidity, and reducing adverse selection and moral hazard in lending. This mechanism suggests that global economic conditions that influence corporate cash flows, such as changes in commodity prices or international trade dynamics, can substantially impact Treasury yields and currency values by affecting corporate investment decisions and the overall economic activity.
Conclusion
Disclaimer: This is not an Investment Advice. Investing and trading in currencies involve inherent risks. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and consider your risk tolerance before engaging in any financial activities.