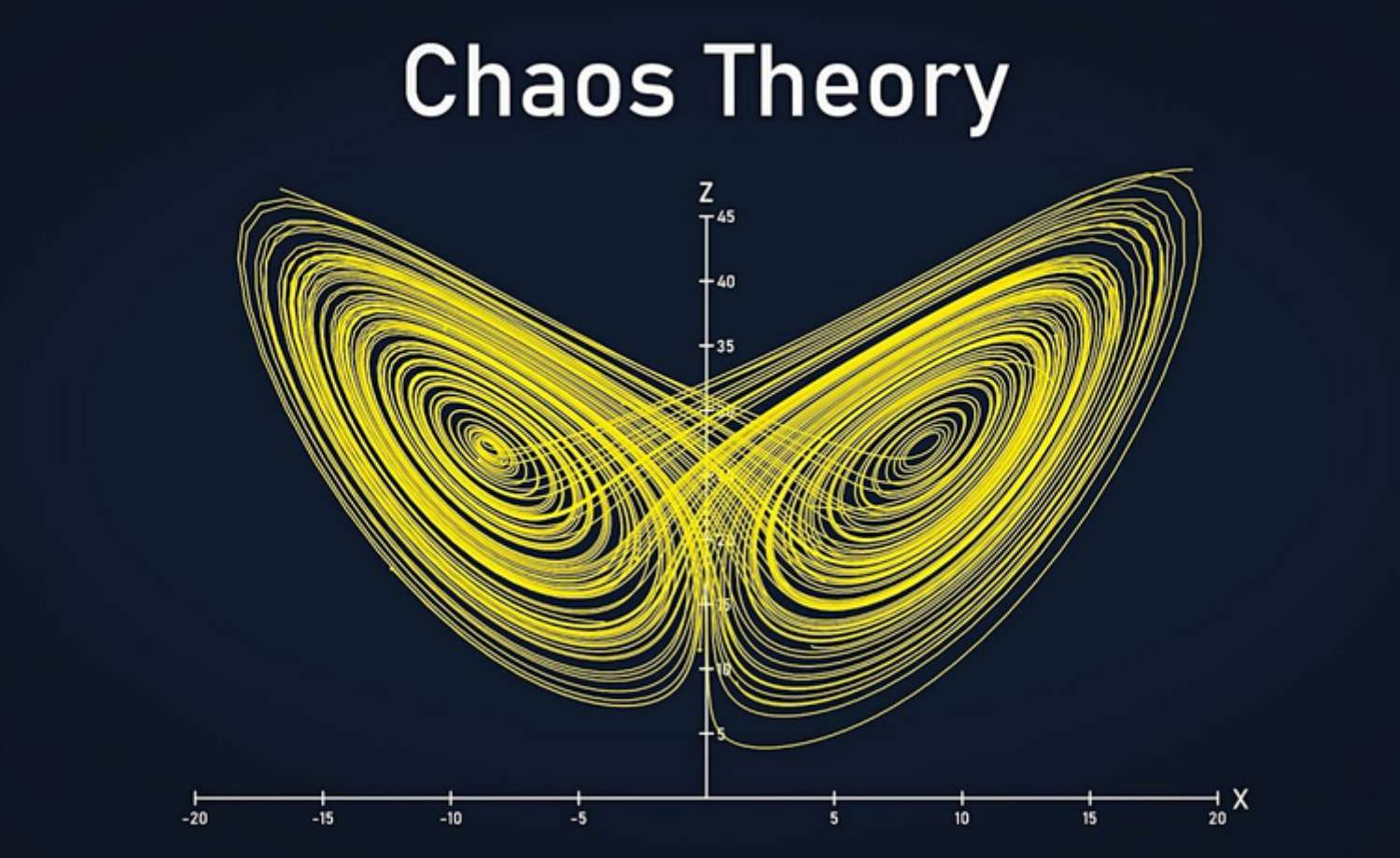
An Overview of Chaos Theory
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of scientific study and branch of mathematics focused on underlying patterns and deterministic laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, and were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. It has applications in various disciplines, including economics.
In finance, chaos theory argues that price is the last thing to change for a security. It seeks to explain the effect of seemingly insignificant factors on complex systems like financial markets, which are often considered chaotic or random occurrences. Chaotic systems are predictable for a while and then appear to become random. The theory has been applied to currency prices and exchange rates, as they are influenced by various factors such as traders’ personal motivations, market sentiment, and economic indicators.
Although chaos theory can provide insights into the behavior of currency prices, it does not offer a straightforward method for predicting specific exchange rates. Instead, it helps to understand the complex dynamics and sensitivities of currency markets, which can be influenced by a multitude of factors.
Chaos theory offers a framework to understand the complex and seemingly unpredictable behavior of financial markets. This interdisciplinary field of study, blending mathematics and scientific inquiry, sheds light on the underlying patterns and deterministic laws governing seemingly chaotic and unpredictable financial systems
Chaos Theory and Its applications in Financial Markets:
Chaos theory has several applications in financial markets, including the Fractal Market Hypothesis, behavioral finance, complex systems analysis, and market psychology. In this response, we will focus on the Fractal Market Hypothesis (FMH) as an example of how chaos theory applies to financial markets.
The Fractal Market Hypothesis is an extension of the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) and was developed by Ed Peters in his 1994 book, “Fractal Market Analysis: Applying Chaos Theory to Investment and Economics”. FMH argues that market prices exhibit fractal properties over time, which can be disrupted when the information sets and time horizons of investors change. According to FMH, convergence of time horizons and information sets toward the short-term during times of heightened market uncertainty can be modeled as a collapse of the fractal structure of market prices. This can produce sudden spikes in market volatility and lack of market liquidity witnessed during crashes and crises.
Chaos theory helps to understand the complex dynamics and sensitivities of financial markets, which can be influenced by a multitude of factors, such as traders’ personal motivations, market sentiment, and economic indicators. Although chaos theory can provide insights into the behavior of financial markets, it does not offer a straightforward method for predicting specific asset prices or market movements. Instead, it helps to understand the underlying patterns and dynamics that govern the seemingly random behavior of financial markets.
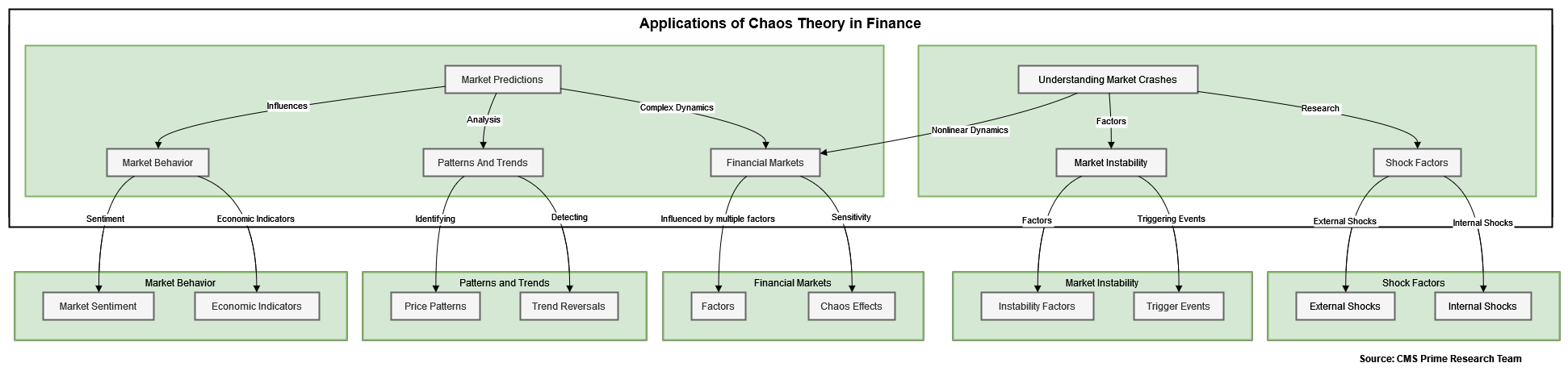
The Fractal Market Hypothesis (FMH), an offshoot of chaos theory, provides insight into the fractal properties of market prices over time. It explains how the structure of these prices can crumble during periods of heightened uncertainty, giving rise to abrupt spikes in market volatility and liquidity challenges
Applications to Finance in context to Market Predictions and Crashes
Chaos theory has been applied to finance in various ways, with some real-world examples including the Fractal Market Hypothesis, market predictions, and understanding market crashes. Here are a few examples:
1.Market Predictions: Chaos theory has been used to understand the complex dynamics and sensitivities of financial markets, which can be influenced by a multitude of factors, such as traders’ personal motivations, market sentiment, and economic indicators. Although chaos theory does not offer a straightforward method for predicting specific asset prices or market movements, it helps to understand the underlying patterns and dynamics that govern the seemingly random behavior of financial markets.
2.Understanding Market Crashes: Chaos theory can help illustrate how seemingly healthy financial markets can suffer sudden shocks and crashes. By studying the complex interdependencies and nonlinear dynamics of financial markets, chaos theory can provide insights into the factors that contribute to market instability and the potential for sudden, dramatic changes in market conditions.
While chaos theory has been applied to finance in various ways, it is important to note that it does not provide a definitive method for predicting market movements or asset prices. Instead, it offers a framework for understanding the complex dynamics and sensitivities of financial markets, which can be influenced by a multitude of factors.
Chaos Theory and Market Crashes:
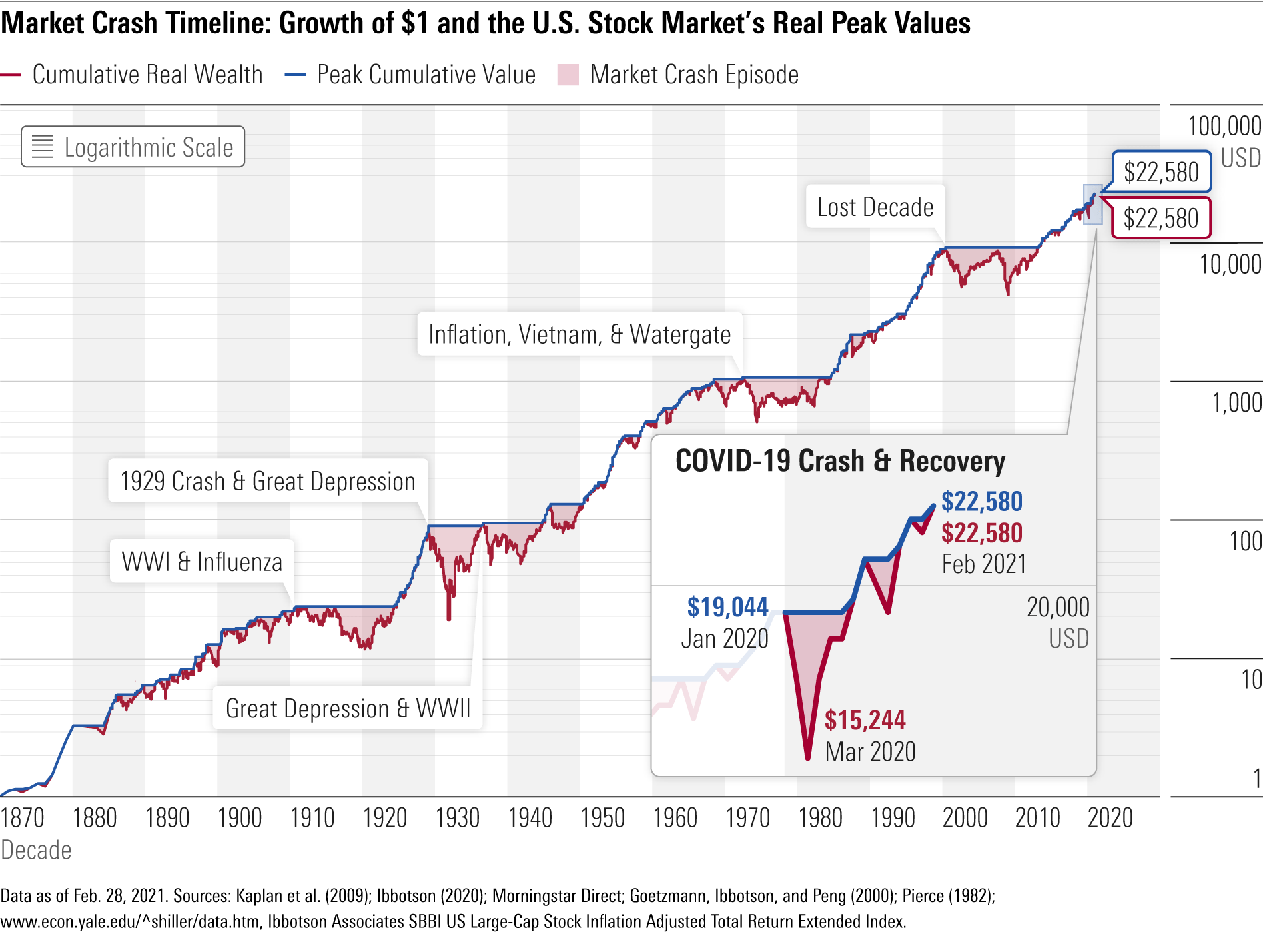
Chaos theory can help explain market crashes by illustrating how seemingly healthy financial markets can suffer sudden shocks and crashes due to their complex interdependencies and nonlinear dynamics. The theory suggests that minor changes in a complex system, such as financial markets, can have significant consequences and push the system far away from its equilibrium.
One example of chaos theory applied to finance is the Fractal Market Hypothesis (FMH), which argues that market prices exhibit fractal properties over time, disrupted when the information sets and time horizons of investors change. FMH helps to explain sudden spikes in market volatility and lack of market liquidity witnessed during crashes and crises.
Chaos theory also highlights that periods of low price volatility do not necessarily reflect the true health of the market, as price is considered the last thing to change for a security. This means that investors may not be able to spot crashes before they happen by solely relying on price indicators.
In summary, chaos theory provides a framework for understanding the complex dynamics and sensitivities of financial markets, which can be influenced by a multitude of factors. By studying these dynamics, chaos theory can offer insights into the factors that contribute to market instability and the potential for sudden, dramatic changes in market conditions. However, it is important to note that chaos theory does not provide a definitive method for predicting market movements or asset prices, but rather helps to understand the underlying patterns and dynamics governing the seemingly random behavior of financial markets.
Financial markets response to market Crashes:
Financial institutions respond to market crashes in various ways to mitigate risks, maintain stability, and ensure the smooth functioning of the financial system. Some of the common responses include:
- Liquidity support: Central banks often provide liquidity support to financial institutions during market crashes to ensure they have enough cash to meet their short-term obligations and maintain stability in the financial system. This can be done through various mechanisms, such as lowering interest rates, buying back government debt, or offering emergency loans to banks.
- Risk management: Financial institutions reassess their risk management strategies during market crashes to better understand and manage their exposure to market risks. This may involve adjusting their investment portfolios, implementing stress tests, and improving their internal risk management practices.
- Regulatory compliance: Financial institutions are required to comply with various regulations and laws designed to prevent financial crises and maintain stability in the financial system. In the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, several major regulations were introduced, such as the Dodd-Frank Act and the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP), which aimed to strengthen the oversight of large banks, financial institutions, and insurance companies.
- Capital and asset management: Financial institutions may need to adjust their capital and asset management strategies during market crashes to maintain their financial health and meet regulatory requirements. This can involve raising additional capital, selling off non-core assets, or reducing their exposure to high-risk investments.
- Cooperation with other financial institutions: In some cases, financial institutions may collaborate with other institutions to provide support during market crashes, such as the Wall Street’s biggest lenders clubbing together to rescue First Republic Bank after its shares crashed, pumping $30bn into it.
It is important to note that the specific response of financial institutions to market crashes may vary depending on the nature and severity of the crash, as well as the individual institution’s risk profile and financial health.
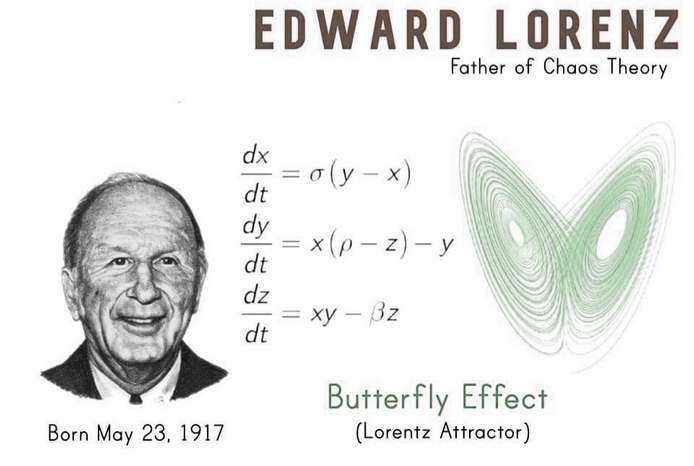
Butterfly Effect and Currency Markets:
The butterfly effect is a concept in chaos theory that suggests small changes in initial conditions can lead to vastly different outcomes in complex systems. In the context of currency markets, the butterfly effect can be seen as small events or changes that may have non-linear impacts on exchange rates and market dynamics. Currency markets are highly complex and interconnected, with participants such as banks, corporations, central banks, investment management firms, hedge funds, retail forex brokers, and investors. These markets facilitate global transactions, including loans, investments, corporate acquisitions, and global trade. While it is difficult to pinpoint specific examples of the butterfly effect in currency markets, it is important to recognize that small events or changes can potentially have significant consequences in these complex systems.
The butterfly effect can manifest in currency markets through various scenarios. Here are a few examples:
- Political events: Unexpected political events, such as elections or policy changes, can lead to fluctuations in currency markets. For example, the Brexit referendum in 2016 led to a significant drop in the value of the British pound against other major currencies.
- Central bank interventions: Central banks can influence currency markets by adjusting interest rates or intervening directly in foreign exchange markets. For instance, in 2003, the Hungarian National Bank intervened in the exchange market to counteract speculative attacks but later announced that it would only intervene in cases of market disturbances.
- Economic data releases: Economic data, such as GDP growth, inflation, and employment figures, can impact currency markets as traders and investors adjust their positions based on the data. For example, better-than-expected economic data from a country can lead to an appreciation of its currency, while disappointing data can result in depreciation.
- Speculative trading: Large-scale speculative trading by hedge funds and other market participants can cause significant fluctuations in currency markets. For example, in 1992, George Soros famously “broke the Bank of England” by betting against the British pound, forcing the UK to withdraw from the European Exchange Rate Mechanism and leading to a sharp depreciation of the pound.
- Natural disasters: Natural disasters can have a butterfly effect on currency markets by disrupting economic activity and causing uncertainty. For example, the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan led to a temporary appreciation of the Japanese yen as investors sought safe-haven assets.
These examples demonstrate how small events or changes can have significant consequences in the complex and interconnected world of currency markets. It is essential for market participants to be aware of the potential butterfly effect and its implications for exchange rates and market dynamics.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, chaos theory serves as a valuable lens through which we can examine the intricate dynamics of financial markets. This interdisciplinary field of study, blending mathematics and scientific inquiry, sheds light on the underlying patterns and deterministic laws governing seemingly chaotic and unpredictable financial systems. By delving into the highly sensitive nature of these systems to initial conditions and the impact of various influencing factors, such as trader motivations and economic indicators, chaos theory deepens our comprehension of market behavior.
The Fractal Market Hypothesis (FMH), an offshoot of chaos theory, provides insight into the fractal properties of market prices over time. It explains how the structure of these prices can crumble during periods of heightened uncertainty, giving rise to abrupt spikes in market volatility and liquidity challenges. FMH underscores the need for market participants to remain vigilant, as market behavior can quickly transition from apparent stability to turbulence.
Furthermore, we’ve explored how financial institutions respond to market crashes. Liquidity support, risk management, regulatory compliance, and collaboration with other institutions are among the strategies employed to mitigate risks and preserve financial stability during crises.
While chaos theory and FMH enhance our understanding of financial markets, it’s crucial to note that they do not provide a crystal ball for predicting specific market movements or asset prices. Instead, they offer a framework for deciphering the intricate dance of variables that shape market behavior.
In navigating the labyrinthine world of finance, chaos theory remains an invaluable tool, offering deeper insights into the complex, interconnected, and often unpredictable nature of financial markets. It reminds us that beneath apparent chaos lie discernible patterns and deterministic laws that can aid us in making more informed decisions and responding effectively to market turbulence.
Disclaimer: This is not an Investment Advice. Investing and trading in currencies involve inherent risks. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and consider your risk tolerance before engaging in any financial activities.