Introduction:
Analyzing the interconnection between the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and currency fluctuations involves understanding how equity markets can influence foreign exchange rates and vice versa. The DJIA, a significant indicator of U.S. economic health and investor sentiment, can impact currency values through various channels.
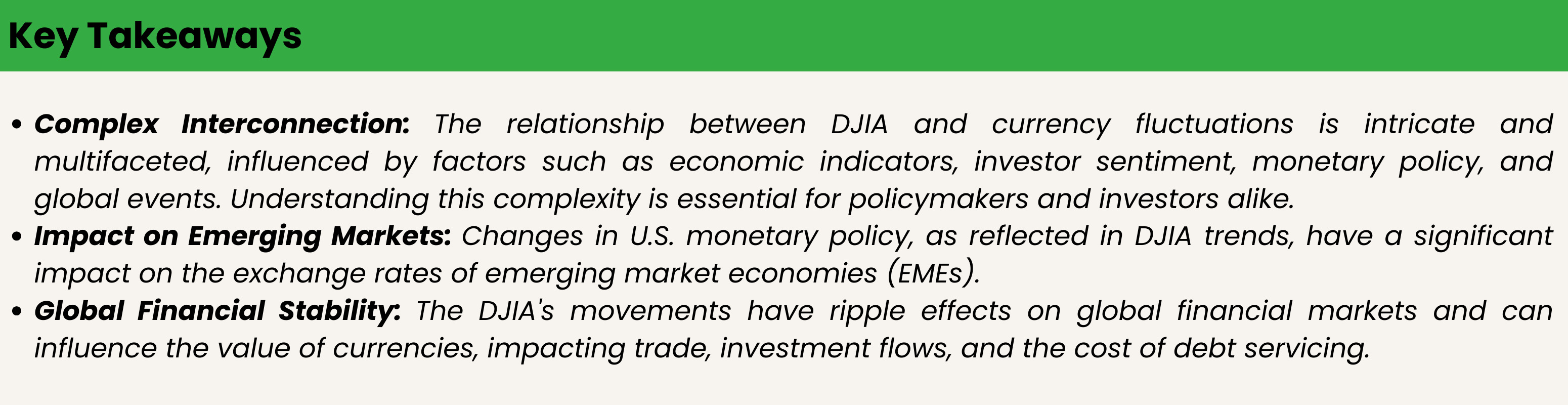
The relationship between the Dow Jones and currency fluctuations is complex and multifaceted. While there is a significant interconnection, it is influenced by a range of factors including macroeconomic news, economic cycles, financial market conditions, and global events. Understanding this relationship requires a holistic approach, considering both the direct and indirect impacts of equity market performance on foreign exchange rates.
DJIA and Currencies-Connecting the Dots
Relationship Between DJIA and Currency Fluctuations:Research indicates a significant relationship between the DJIA and industrial production in the U.S., suggesting a linkage between stock market performance and economic activity. This connection can indirectly influence currency values as economic strength or weakness tends to affect investor sentiment towards a country’s currency.The DJIA’s movements reflect broader economic trends, including inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical events, which can directly impact exchange rates.
Exchange Rates and Macroeconomic Fundamentals:Contrary to the perception that exchange rates are mostly disconnected from macroeconomic fundamentals, recent studies argue that macroeconomic indicators significantly impact exchange rate variations. For instance, announcements about macroeconomic indicators can explain a substantial portion of the variation in currency risk premia, which in turn affects exchange rates.Since 2001, macroeconomic news has explained about 70% of the variation in quarterly exchange rate changes for advanced economies’ currencies against the U.S. dollar. During U.S. recessions, this explanatory power increases to 84%.
Financial Channel and Exchange Rate Fluctuations:Exchange rate fluctuations influence economic activity not only through the standard trade channel but also via a financial channel. This channel operates through the impact of exchange rate changes on borrowers’ balance sheets and lenders’ risk-taking capacities.Such fluctuations, particularly in the U.S. dollar, can significantly affect cross-border bank flows, illustrating the interconnected nature of equity markets and foreign exchange rates.
Impact of Economic Downturns and Financial Uncertainty:During economic downturns and periods of financial uncertainty, macroeconomic news and surprises have even greater explanatory power over exchange rate changes. This suggests that during these periods, currency markets are more sensitive to macroeconomic indicators.
Example of Direct Impact:An example of the direct impact of the DJIA on currency exchange rates can be seen during significant market events. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the DJIA experienced substantial drops (e.g., 33% in March 2020), which would have had profound implications on currency volatility and exchange rate predictions
Adaptive Capacity: DJIA's Role in Currency Interconnectedness
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a key determinant of the value of the US dollar on the global financial market. The DJIA is a gauge of the health of the US economy, and it reflects significant economic indicators and investors’ emotions. A strong performance in DJIA usually means that economic activities are moving at a higher rate hence predicting increased interest in future, improved investment returns, and stability in economy. This in turn makes the United States currency more desirable to investors because they expect higher profits and lower risk. On the contrary, when DJIA shows weakness or decline, it raises questions about economic slow down or uncertainty that can result into capital outflows with associated dollar depreciation.
Moreover, this link is underpinned by Federal Reserve’s monetary policy which closely tracks the conduct of business as signaled by DJIA. Bullish stock market conditions may create an anticipation for tighter monetary conditions leading to higher interest rates thus more appealing dollar by those searching for yields. Additionally, US economy flexibility as per how it performs in DJIA underpins its strength. Confidence in dollar grows when there is resilience and adaptability seen from a healthy DJIA. Conversely, a struggling equity market might suggest difficulties in adapting, thereby weakening the dollar’s appeal. Furthermore, in today’s globalized world, external factors such as global economic and geopolitical events exert considerable influence on the DJIA and, consequently, the U.S. dollar. These events can impact the U.S. economy and its currency value, as exemplified by a global economic downturn originating outside the U.S., which can lead to a fall in the DJIA and impact the dollar’s value as risk aversion increases. Overall, the DJIA’s performance intertwines with various economic indicators, investor sentiment, monetary policy expectations, and global interconnectedness to significantly influence the U.S. dollar’s value, making it a critical factor for financial markets and policymakers alike to monitor closely.
DJIA Trends and Emerging Market Currency Exchange Rates Impact
Changes in U.S. monetary policy, particularly as reflected in trends of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), can significantly impact the exchange rates of emerging market economies (EMEs). This impact is shaped by a dynamic interplay of risk-return tradeoffs and market volatility, which are essential components in understanding these relationships from a dynamical perspective:
Financial Channels and Global Financial Cycle:
- U.S. monetary policy affects foreign economies, especially EMEs, through financial channels. When U.S. policy tightens, it can result in declines in international risky asset prices, tighter financial conditions, and capital outflows from EMEs. This phenomenon, known as the Global Financial Cycle, disproportionately impacts EMEs due to the larger effect of U.S. policy rates on rates in EMEs.
Spillover Effects on EMEs:
- U.S. monetary policy can lead to a fall in EME output, comparable in magnitude to declines in U.S. GDP. The impact remains significant even after the effect of the shock on interest rates dissipates. This demonstrates the persistence and magnitude of U.S. monetary policy spillovers on EMEs.
- Two primary transmission channels are identified: the trade channel, where lower U.S. demand impacts EME exports, and the financial channel, where increased credit spreads and higher UIP risk premia slow down investment and economic activity in EMEs.
Impact of Negative Growth/Risk Shocks:
- Several episodes, including the European debt crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic, saw EME currencies depreciate against the dollar due to negative growth/risk shocks, despite lower U.S. yields. These events highlight the dominant role of risk premiums in driving EME currency movements during times of global uncertainty.
Influence of Monetary Shocks and Domestic Conditions in EMEs:
- The effect of U.S. monetary policy on EMEs depends on the nature of the interest rate changes (growth prospects vs. inflation concerns) and the domestic conditions in the EMEs themselves. EMEs with higher macroeconomic vulnerabilities are more sensitive to changes in U.S. interest rates.
In summary, changes in U.S. monetary policy, inferred from DJIA trends, affect the exchange rates of EMEs through complex, interconnected mechanisms involving trade and financial channels, the balance sheet health of EME borrowers, and the nature of global risk perceptions. The extent and nature of these effects are influenced by the underlying economic conditions in both the U.S. and EMEs, and the type of monetary shocks (growth-driven or inflation-driven), highlighting the dynamical aspects of risk-return tradeoff and market volatility in these relationships.
Understanding the Interplay: DJIA and Currency Exchange Rates
The interconnectedness of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and currency exchange rates plays a significant role in influencing global financial stability and shaping monetary policy decisions. This relationship is multifaceted, reflecting the complex dynamics of global financial markets, and is particularly impacted during periods of financial crises or economic uncertainty.
Impact of the DJIA on Global Financial Markets:
- The DJIA, representing major American corporations, is a barometer of the U.S. economic health and investor sentiment. Movements in the DJIA can reflect underlying economic conditions, which in turn influence global financial markets. When the DJIA experiences volatility, it can cause ripple effects globally, affecting investor confidence and market stability worldwide.
Currency Exchange Rates and Global Financial Stability:
- The value of a currency, such as the U.S. dollar, is crucial in global financial markets. Significant changes in currency values can impact global trade, investment flows, and the cost of debt servicing. For instance, a strong U.S. dollar can lead to tighter financial conditions globally, as it increases the cost of dollar-denominated debt for foreign borrowers and affects the relative competitiveness of exports.
Monetary Policy and Exchange Rates:
- Central banks’ monetary policies significantly influence currency exchange rates. For example, when the U.S. Federal Reserve adjusts interest rates, it can lead to changes in the value of the dollar, affecting global currency markets. Higher U.S. interest rates can attract more foreign investment into dollar-denominated assets, strengthening the dollar. This can have a knock-on effect on emerging markets, which often struggle with higher costs for servicing dollar-denominated debt and can face capital outflows.
Risks and Challenges for Emerging Markets:
- Emerging and developing economies are particularly susceptible to fluctuations in the DJIA and currency exchange rates. A surging dollar, for instance, can lead to rapidly depleting foreign reserves, increased costs for debt servicing, and the potential for debt defaults. This scenario can cause significant financial instability in these economies, which often rely heavily on external financing and are more vulnerable to global financial conditions.
Economic Uncertainty and Coherent Biases:
- Economic uncertainty, such as that brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic, can exacerbate the interplay between stock indices like the DJIA and currency exchange rates. Investors’ biases towards safe-haven assets like the U.S. dollar can intensify during times of crisis, leading to greater volatility and unpredictability in global markets. Such biases, while coherent in the short term, can lead to misalignments in currency values and stock market valuations, complicating monetary policy decisions and financial stability efforts.
Overall, the interconnection between the DJIA and currency exchange rates is a critical component in the global financial system, influencing monetary policy decisions and the broader economic environment. Policymakers and investors must navigate this complex landscape, balancing short-term responses to market movements with longer-term strategies for financial stability and economic growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and currency exchange rates is a crucial factor in shaping global financial stability and influencing monetary policy decisions. This interplay is characterized by multifaceted dynamics, where movements in the DJIA reflect economic conditions and investor sentiment, impacting currency values and global financial markets. The DJIA’s influence extends beyond borders, affecting emerging markets, and poses risks and challenges during periods of economic uncertainty. As central banks adjust their policies and investors respond to market fluctuations, the interconnectedness of these factors underscores the need for a nuanced approach to navigating the complexities of the global financial landscape.
Disclaimer: This is not an Investment Advice. Investing and trading in currencies involve inherent risks. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and consider your risk tolerance before engaging in any financial activities.