Introduction:
Qualitative assessment of trading strategy development is about looking into the non-quantifiable components of a strategy. Here are two ways to do this:
1. Assessing the Strategy’s Underlying Logic and Consistency: This means knowing why the strategy is, what it is intended to achieve and how it reacts to different market conditions. However, it is essential to ensure that the strategy is uniform, objective, and founded on market analysis principles. This might include examining whether the strategy uses fundamental or technical analysis, its risk management strategy, or its flexibility in changing market conditions.
2. Evaluating the Strategy’s Performance Over Time: This calls for assessing the impact the strategy has generated and how well it has performed in different markets conditions. This will allow to measure the robustness of the strategy and its consistent results. For instance, the strategy’s win ratio payoff ratio, maximum drawdown, and rate of return are some of the key performance indicators that investors can use. The strategy’s performance needs to be considered compared to the risk it involved, as some high-gain but risky strategy is not applicable for all kinds of investors.
Recollect, qualitative evaluation is arbitrary and can be affected by personal prejudices. Hence, it is essential to employ systematic approach, and take into account various factors while assessing a trading strategy.
Key Components of Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis of a trading strategy involves evaluating the non-quantifiable aspects of the strategy. Here are some key components of such an analysis:
1. Management and Execution: This involves assessing the people who are managing and executing the strategy. It’s important to consider their expertise, experience, and track record. This could involve evaluating their decision-making processes, their ability to adapt to changing market conditions, and their approach to risk management.
3. Performance Over Time: This involves looking at how the strategy has performed over a significant period of time, including during different market conditions. This can help to assess the strategy’s robustness and its ability to deliver consistent results. Key performance indicators to consider might include the strategy’s win ratio, payoff ratio, maximum drawdown, and rate of return. It’s also important to consider the strategy’s performance in relation to its risk level.
4. Industry Analysis: This involves evaluating the industry in which the strategy is being applied. It’s important to consider the industry’s growth potential, competitive dynamics, and key trends. This could involve evaluating the strategy’s approach to identifying and capitalizing on industry trends, its ability to navigate competitive dynamics, and its adaptability to changes in the industry.
Remember, qualitative analysis is subjective and can be influenced by individual biases. Therefore, it’s important to use a systematic approach and consider a range of different factors when evaluating a trading strategy.
Some examples of qualitative factors for Strategy Development
Qualitative issues play a critical role in assessing a trading strategy, encompassing non-quantifiable factors that contribute to its overall effectiveness. These include the quality of management, which hinges on the expertise, experience, and track record of those overseeing and executing the strategy. Their decision-making skills, adaptability to market changes, and risk management attitudes are crucial. The underlying logic and consistency of the strategy are also important, requiring a clear understanding of its objectives, reasoning, and response to various market conditions. The strategy should be consistent, objective, and based on solid market analysis principles.
Another key aspect is customer satisfaction, which could refer to investors or other stakeholders. High levels of satisfaction suggest that the strategy is effective and well-received. Corporate governance, including the function of the company’s board of directors, its social responsibility policies, and compliance with regulatory standards, can also impact the performance of a trading strategy.
Additionally, industry analysis is vital, encompassing the growth potential of the industry, competitive dynamics, and key trends. This involves examining the strategy’s methods for tracking trends, adapting to competitive and industry changes. Furthermore, company news and major financial events, such as mergers, acquisitions, or regulatory changes, can significantly influence a company’s trading strategy. It’s important to consider the implications of these events on the strategy.
However, it’s important to note that qualitative analysis is subjective and can be influenced by personal biases. Therefore, a systematic approach is necessary, incorporating various factors for a comprehensive assessment of a trading strategy.
Combining Qualitative and Quantitative-How?
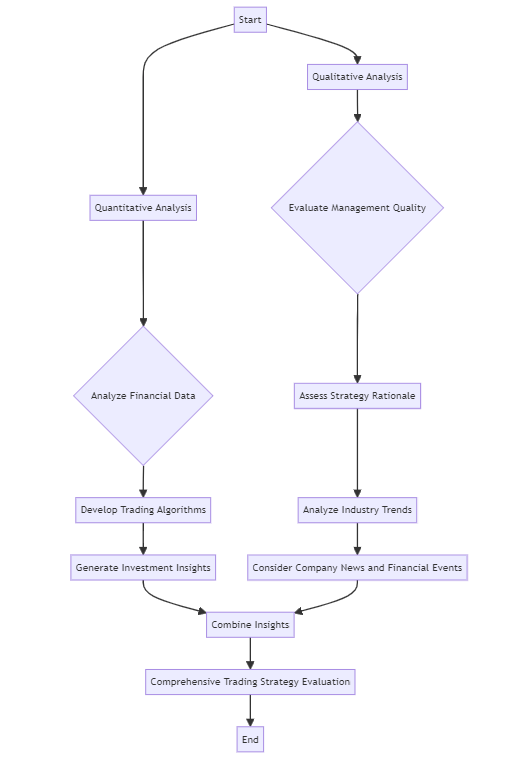
Yes, qualitative factors can indeed be used in combination with quantitative factors to evaluate a trading strategy. This approach provides a more comprehensive assessment of the strategy, as it considers both numerical data and non-numeric aspects.
Quantitative analysis uses mathematical and statistical methods to evaluate a trading strategy. It involves analyzing financial data, such as historical investment and stock market data, to develop trading algorithms and computer models. These models generate information that helps investors analyze investment opportunities and develop trading strategies.
On the other hand, qualitative analysis focuses on non-numeric aspects that can impact a trading strategy. These may include the quality of management, the rationale behind the strategy, customer satisfaction, corporate governance, industry trends, and significant company news or financial events.
Combining these two types of analysis can provide a more holistic view of a trading strategy. Quantitative analysis can identify potential investments, while qualitative analysis can provide additional insights that numerical data may not capture. For instance, qualitative analysis can shed light on the strategy’s adaptability to changing market conditions, the quality of decision-making processes, and the strategy’s response to significant events.
However, it’s important to note that both types of analysis have their limitations. Quantitative analysis may not account for all relevant factors, especially those that are difficult to measure or quantify. Meanwhile, qualitative analysis is subjective and can be influenced by individual biases. Therefore, using a combination of both can help to mitigate these limitations and provide a more balanced and comprehensive evaluation of a trading strategy.
Conclusion
Disclaimer: This is not an Investment Advice. Investing and trading in currencies involve inherent risks. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and consider your risk tolerance before engaging in any financial activities.