Harnessing the Buffett Indicator for currency valuation plays an important role in understanding the usefulness of the indicator. The Buffett Indicator, which is named after Warren Buffett, is a tool used to assess market conditions. It does this by comparing the market value of traded stocks in a country to that countrys Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This ratio helps us understand the valuation of the market. When the ratio is high, it suggests that the market may be overvalued, while a low ratio indicates undervaluation. Warren Buffett himself has praised this indicator as a measure of valuations in time. Although it has its limitations many investors find the Buffett Indicator helpful, for evaluating long term stock market valuations and identifying investment opportunities.
Concurrently, currency markets form a dynamic ecosystem where global currencies are exchanged. Exchange rates, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and JPY/USD, are indicative of economic conditions, geopolitical factors, interest rate differentials, and market sentiment. These rates hold substantial importance for international businesses involved in trade, as well as for investors navigating the intricate landscape of the forex market.
The interplay between the Buffett Indicator and currency markets unveils a complex connection where economic indicators, market sentiment, and geopolitical dynamics intersect. Their mutual influence extends to investment decisions, risk management strategies, and the broader assessment of global economic health. Recognizing these multifaceted relationships is vital for informed decision-making across financial sectors on a global scale.
Buffett once said in an article in “Fortune” magazine in 2001 that when the Buffett indicator is 100%, it indicates that the valuation of US stocks is reasonable, and it may be good to buy at 70% or 80%. However, buying US stocks at around 200% is tantamount to “setting yourself on fire
Warren Buffett’s Perspective
Renowned investor Warren Buffett considers the Buffett Indicator as a tool for assessing market conditions. In a 2001 interview he described it as ” the single measure of where valuations stand at any given moment.” However it is important to note that no one metric can provide an assessment of market conditions.
Calculation and Interpretation
To calculate the Buffett Indicator divide the market value of all traded stocks in a country by its GDP. Higher values of this ratio suggest overvaluation while lower values indicate undervaluation. While there are limitations to this indicator it is regarded as useful for evaluating long term stock market valuations and identifying investment opportunities.
Historical Trends and Patterns
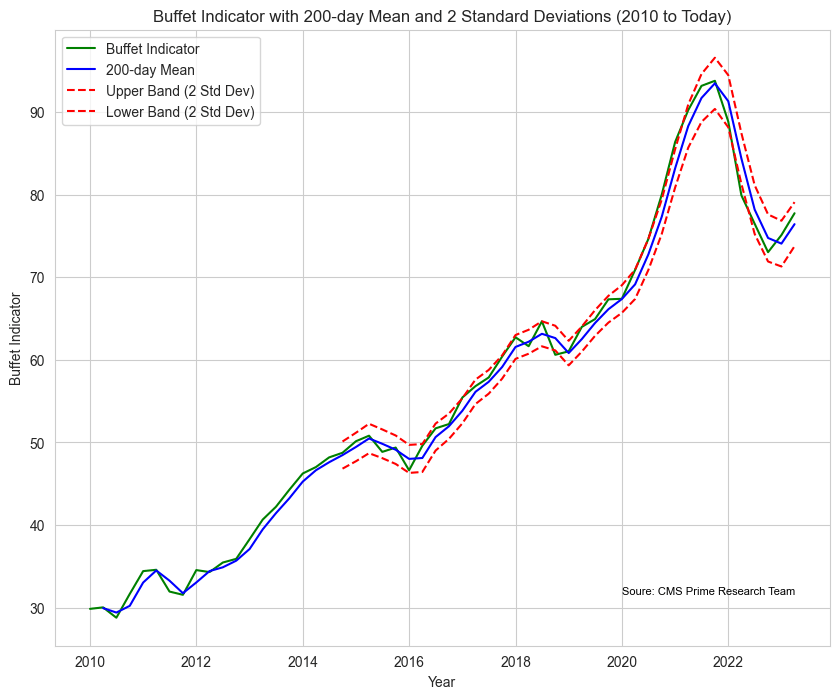
Over time the Buffett Indicator has demonstrated its ability to predict market crashes, such as, during the dot com bubble. However it’s crucial to take into account factors and not depend on the indicator when making investment choices. The Buffett Indicator has consistently exceeded 100% for a duration, which suggests that stocks have been overpriced for years. Nevertheless it continues to serve as an instrument for investors to assess market conditions and make informed judgments.
The interplay between the Buffett Indicator and currency markets unveils a complex connection where economic indicators, market sentiment, and geopolitical dynamics intersect.
Currency Evaluation and the Buffett Indicator
In the realm of currency valuation, the Buffett Indicator’s significance lies in its capacity to offer a broader contextual lens for evaluating the strength and prospects of specific currency pairs. Beyond the conventional focus on exchange rate movements, incorporating the indicator’s insights allows for a more holistic understanding of the economic underpinnings driving currency dynamics.
When the Buffett Indicator signals market overvaluation, it prompts consideration of potential economic imbalances that could indirectly influence currency performance. An overvalued equity market might suggest misalignment between financial market exuberance and underlying economic fundamentals. This, in turn, could impact investor sentiment, affecting the demand for the associated currency.
Moreover, when growth rotation trends drive shifts in currency strength, the Buffett Indicator’s historical perspective becomes invaluable. It aids in assessing whether these trends align with established long-term economic patterns or represent deviations that require closer examination. By contextualizing current currency valuation shifts within the indicator’s historical framework, traders and investors gain a more nuanced perspective on potential implications.
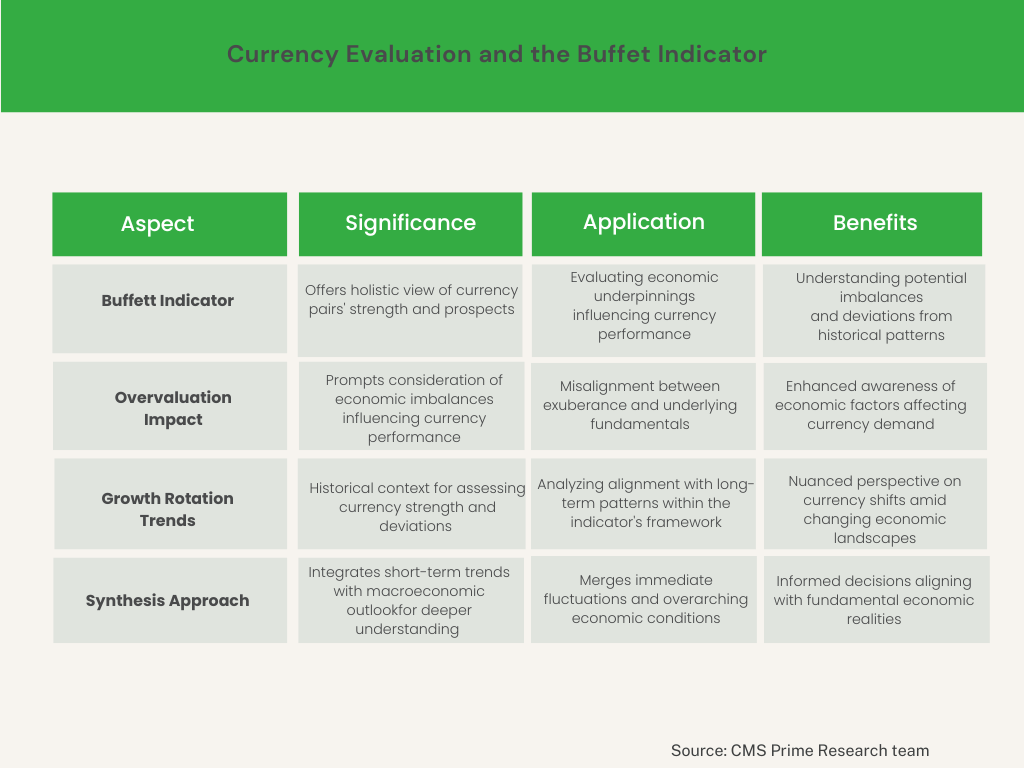
By incorporating the Buffett Indicator into currency valuation assessments, traders and investors merge short-term currency pair movements with a broader macroeconomic outlook. This synthesis provides a deeper understanding of how immediate trends align with fundamental economic conditions. Consequently, it empowers decision-makers to navigate currency markets more prudently by factoring in both immediate fluctuations and overarching economic considerations.
In conclusion, the Buffett Indicator’s application extends seamlessly into the realm of currency valuation, enhancing analyses with a broader macroeconomic perspective. Its ability to illuminate potential market imbalances and provide historical context aids traders and investors in making informed decisions. As global financial markets remain intricately interconnected, leveraging tools like the Buffett Indicator offers a robust approach to comprehending the multifaceted landscape of currency valuation.
Market Analysis and Insights
Market Valuation Context: In the realm of currency markets, the Buffett Indicator’s application can offer a broader context for evaluating the performance of specific currency pairs. If the indicator suggests that the stock market is overvalued relative to the GDP, it could indirectly impact investor sentiment and risk appetite, potentially influencing the strength of certain currencies. Traders and investors could consider whether these broader valuation conditions align with the performance of specific currency pairs.
Global Economic Impact: Just as in the stock market scenario, the Buffett Indicator can shed light on how currency performance aligns with overall economic health. If growth rotation trends are driving shifts away from the U.S. dollar, the indicator’s insights can help investors assess whether these shifts are rationalized by broader economic fundamentals or if they might indicate potential imbalances.
Safe-Haven Considerations: Currency pairs often reflect global risk sentiment. The Buffett Indicator’s insights can impact decisions related to safe-haven currencies. For instance, if experts are bullish on the yen due to risk-off sentiments and the Buffett Indicator suggests market overvaluation, this might reinforce the appeal of the yen as a safe-haven asset.
Long-Term Perspective: The historical context provided by the Buffett Indicator can guide currency traders in understanding whether the current trends in currency pairs align with long-term economic patterns or if they might be outliers.
This historical context can be particularly useful for investors seeking to navigate short-term fluctuations within a broader economic framework.
Diversification and Risk Management: Currency trading involves assessing risks associated with currency pairs. Incorporating the Buffett Indicator’s insights into the analysis can assist traders in assessing risk and diversifying their portfolios effectively. If the indicator suggests overvaluation in certain markets, traders might adjust their currency exposure to manage potential risks.
Incorporating the Buffett Indicator into currency market analysis provides a comprehensive perspective that goes beyond immediate currency pair movements. It encourages traders and investors to consider the interplay between broader market valuations, economic fundamentals, and short-term currency trends, thereby aiding in making more informed decisions in the dynamic world of currency trading.
Risk Factors and Considerations
Potential Risks Associated with the Buffett Indicator
It’s important to be aware of the risks that come with relying on the Buffett Indicator. This indicator does have its limitations. For instance it focuses on GDP measurements that exclude income from overseas while market capitalizations of companies take into account both foreign operations. It’s also worth noting that no single metric can provide a comprehensive assessment of market conditions. As investors it is crucial to consider factors and indicators before making any investment decisions.
Understanding Currency Valuations and Precious Metal Prices
When interpreting currency valuations and precious metal prices caution should be exercised since multiple factors can influence these values. Economic indicators, geopolitical events and monetary policies can all have an impact on currency values. Similarly factors such as supply and demand dynamics, central bank actions and even the strength of the U.S. Dollar can affect metal prices.
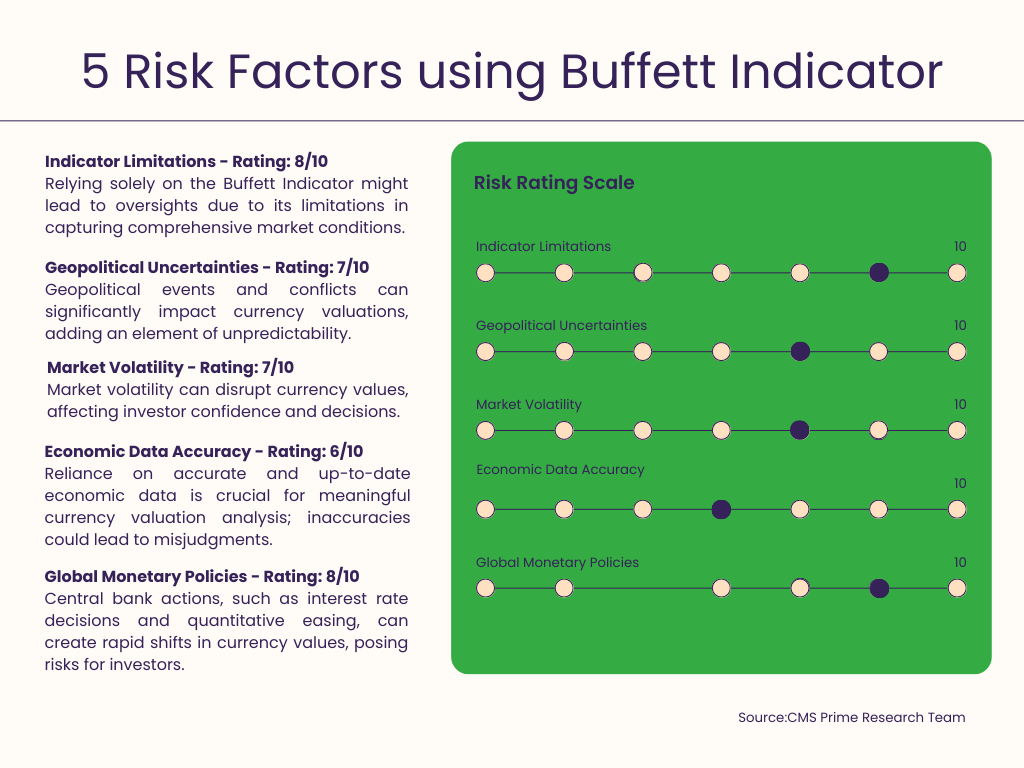
Market Volatility, Geopolitical Uncertainties and Other Influential Factors
Financial markets are susceptible to impacts from sources like market volatility, geopolitical uncertainties and other factors. For instance political instability tends to lead to currency depreciation while stability and cooperation often result in appreciation. Additionally banks monetary policies including decisions on interest rates or quantitative easing measures play a role in shaping currency values. Therefore it is essential for investors to carefully consider these factors along with their effects on stock markets as well as currency and precious metals markets when making investment decisions.
Conclusion
The Buffett Indicator is a tool for assessing market conditions and investment opportunities by comparing the market value of publicly traded stocks to a countrys GDP. However it’s important to note that relying solely on this indicator can be risky. Investors should also consider factors and indicators when making their investment decisions.
Currency valuation in the market is influenced by factors like interest rates, inflation, economic indicators, political stability and market sentiment. Understanding these factors and their impact on currency valuations can assist investors and traders in making informed decisions.
When interpreting metal prices, such as gold, silver and platinum it’s crucial to consider factors like supply and demand dynamics, central bank actions and the strength of the U.S. Dollar. Investors need to exercise caution and take these factors into account while making investment decisions related to metals.
To make decisions in investments it’s essential for investors to stay updated with current information and seek advice from experts. By recognizing the limitations of indicators, like the Buffett Indicator while considering factors affecting currency valuations and precious metal prices simultaneously, investors can navigate markets more effectively.


